How to operate a drone is a question many ask, and the answer encompasses far more than simply pushing buttons. It’s about understanding the technology, mastering the controls, and adhering to safety and legal regulations. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, taking you from pre-flight checks and basic navigation to advanced techniques and legal compliance, ensuring you can confidently and responsibly take to the skies.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone which covers essential pre-flight checks and flight maneuvers. Mastering these techniques ensures safe and effective drone operation.
From understanding the intricacies of drone controls like throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll, to mastering advanced flight modes and utilizing onboard camera systems, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to operate your drone safely and effectively. We’ll explore essential pre-flight checklists, emergency procedures, and legal considerations, transforming you from a novice into a competent drone pilot.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, verifying system functionality, and understanding potential hazards. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents and equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection involves several key steps to ensure your drone is in optimal condition for flight. This process mitigates potential risks and maximizes the chances of a successful flight.
| Step | Check | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Battery Level | Check the battery voltage and ensure it’s sufficiently charged for the planned flight duration. | Record battery voltage; proceed if above minimum recommended voltage. |
| 2 | Propeller Inspection | Visually inspect each propeller for cracks, damage, or debris. | Replace any damaged propellers. |
| 3 | GPS Signal Strength | Verify a strong GPS signal is acquired by the drone. Sufficient satellites should be locked. | Ensure at least 6-8 satellites are acquired for stable flight. If not, find a location with better GPS reception. |
| 4 | Gimbal Functionality (if applicable) | Test the gimbal’s movement and ensure it functions smoothly. | Check for any binding or unusual noises. |
| 5 | Camera Functionality (if applicable) | Test the camera to ensure it’s recording properly and the image is clear. | Check recording resolution and settings. |
| 6 | Drone Body Inspection | Check for any physical damage to the drone body or components. | Address any damage before flight. |
| 7 | Radio Control Connection | Verify a strong connection between the remote controller and the drone. | Check for signal strength indicators on both the remote and the drone. |
Safe Takeoff Procedure
A smooth and controlled takeoff is essential for safe drone operation. This minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures a stable flight.
- Ensure you are in a safe and open area, away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the remote controller first, then the drone.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock and the drone to initialize.
- Carefully lift the drone off the ground using the throttle control, maintaining a slow and steady ascent.
- Once airborne, perform a brief hover check to ensure stability before initiating your flight plan.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. Having a plan in place reduces the impact of unexpected events.
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately if you lose signal. If RTH fails, prepare for a controlled descent.
- Low Battery: Immediately initiate RTH if the battery level reaches a critical threshold. Plan your flights with ample battery capacity to account for unforeseen delays.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section covers the basic controls, GPS navigation, and waypoint programming.
Basic Drone Controls
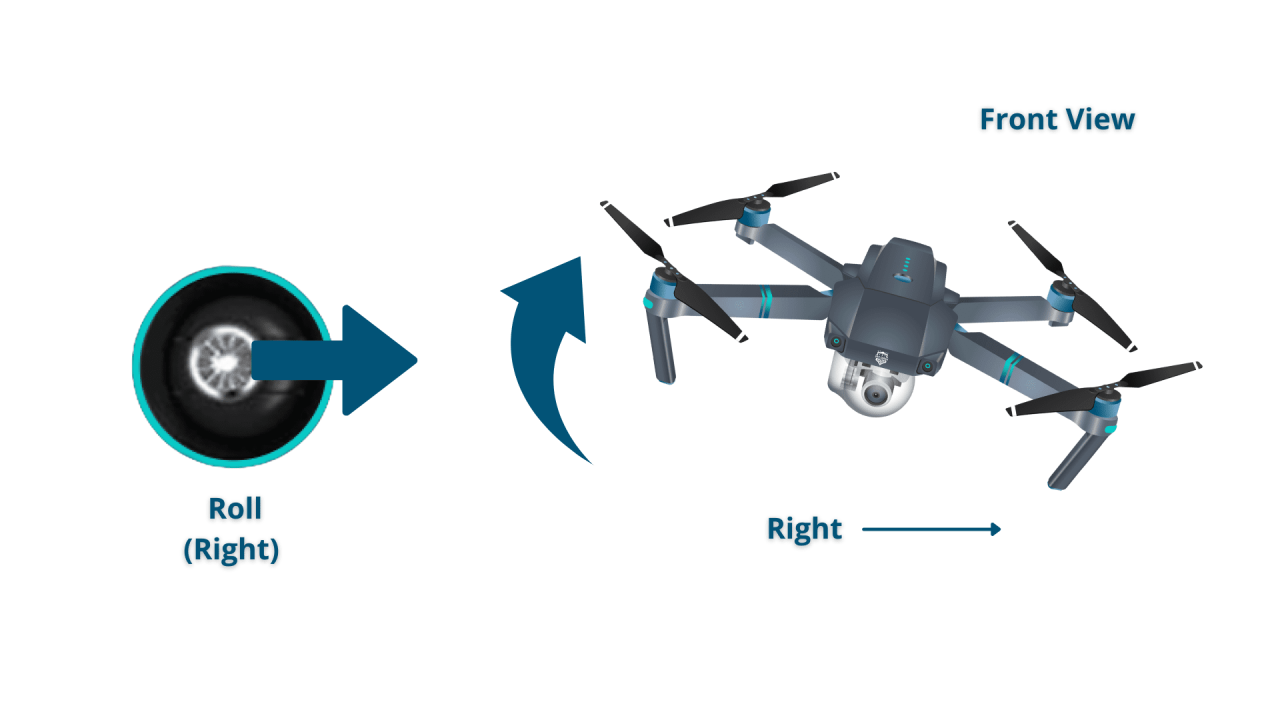
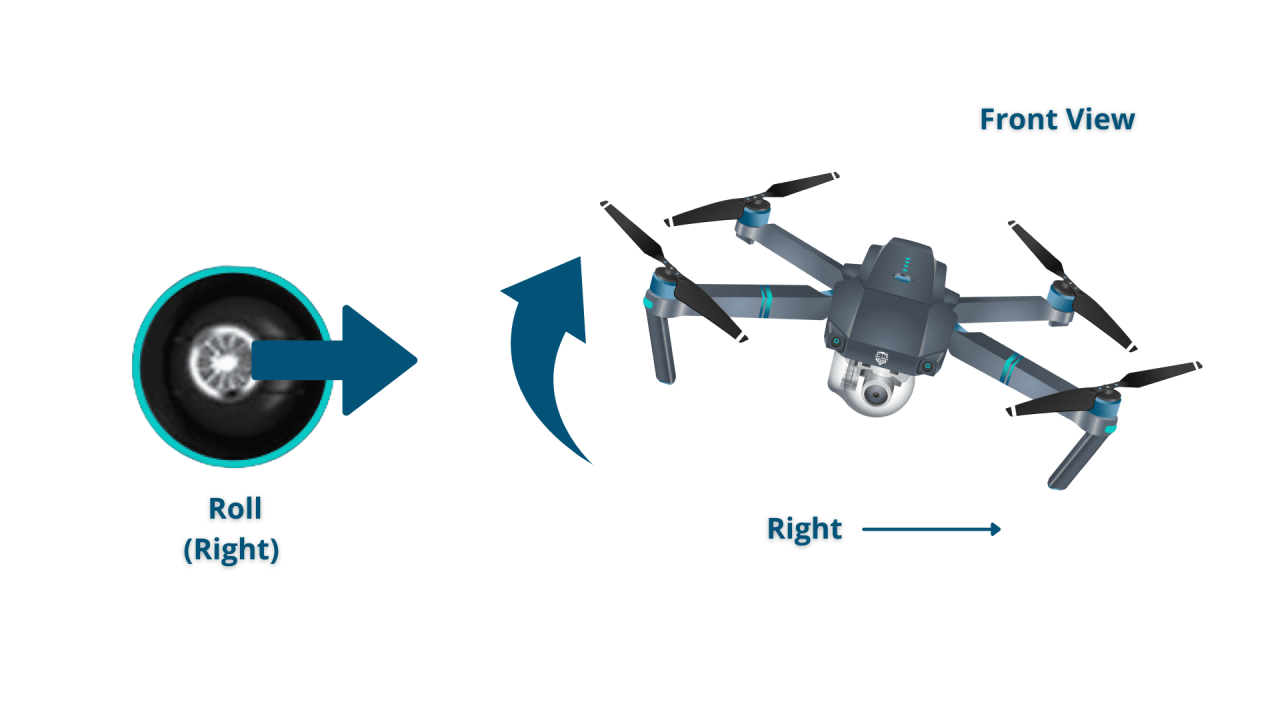
Most drones use a similar set of controls. Understanding these is essential for maintaining control and stability during flight.
| Control | Function |
|---|---|
| Throttle | Controls the altitude of the drone; up increases altitude, down decreases. |
| Yaw | Controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis (turning left or right). |
| Pitch | Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward. |
| Roll | Controls the drone’s movement left and right. |
GPS Navigation and Waypoints
GPS coordinates allow for precise navigation and automated flight paths. Waypoints are pre-programmed locations that the drone will automatically navigate to.
Many drone applications allow you to input GPS coordinates directly or to create a flight path by setting a series of waypoints. The drone will then autonomously follow this path, making complex aerial shots easier to achieve. Accuracy depends on GPS signal strength and environmental factors.
Maintaining Stable Flight and Obstacle Avoidance
Maintaining a stable flight and avoiding obstacles requires practice and awareness. Smooth control inputs and consistent monitoring of the drone’s surroundings are key.
Many modern drones incorporate obstacle avoidance systems using sensors to detect and avoid collisions. However, pilot awareness and responsible flying practices remain crucial. Always maintain visual contact with the drone, and avoid flying in areas with numerous obstacles.
Flight Modes and Features
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios. Advanced drones often include features that enhance safety and flight capabilities.
Flight Modes
Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, making it easier to control the drone. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and more agile maneuvers. Other modes might include GPS mode, which relies on satellite positioning for stability, and attitude mode, which uses onboard sensors for stability regardless of GPS signal.
Advanced Drone Features
Modern drones frequently incorporate advanced features to improve safety and flight capabilities.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Sensors detect nearby objects, allowing the drone to automatically avoid collisions.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): The drone automatically returns to its takeoff point if the signal is lost or the battery is low.
- Follow Me: The drone automatically follows a designated subject, such as a person or vehicle.
Camera Systems and Settings
Drone cameras vary widely in resolution, video recording modes, and image stabilization. Understanding these features is essential for capturing high-quality aerial footage.
Higher resolution cameras provide greater detail, while features like 4K video capture provide smoother, higher-quality video. Image stabilization systems help minimize camera shake during flight.
Drone Model Comparison
| Drone Model | Camera Resolution | Flight Time | Obstacle Avoidance | RTH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drone A | 4K | 30 minutes | Yes | Yes |
| Drone B | 1080p | 25 minutes | No | Yes |
| Drone C | 4K | 35 minutes | Yes | Yes |
Drone Photography and Videography

Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings, composition, and editing techniques.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Achieving professional-looking aerial shots requires careful planning and execution. Understanding factors such as lighting, composition, and camera settings are crucial.
Consider the “rule of thirds” for composition, ensuring the subject isn’t centered but rather placed at one of the intersecting points. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create dynamic shots. Proper lighting is also essential for high-quality imagery.
Camera Angles and Shots
Various camera angles and shots can significantly impact the storytelling and visual appeal of your aerial footage.
- Establishing Shots: Wide shots that show the overall context of a scene.
- Close-ups: Detailed shots that highlight specific features or subjects.
- Tracking Shots: Smooth, continuous shots that follow a moving subject.
Lighting and Composition
Good lighting and composition are fundamental to compelling aerial photography and videography. The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) often provides the most aesthetically pleasing light.
Editing Aerial Footage
Post-production editing enhances the quality and storytelling of aerial footage.
Software such as Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and Final Cut Pro are commonly used for editing drone footage. Color grading, stabilization, and adding music and sound effects can significantly improve the final product.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance

Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. Failure to comply can result in serious consequences.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
- Register your drone with the relevant aviation authority.
- Obtain necessary permits and licenses for commercial drone operations.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Adhere to airspace restrictions and prohibited areas.
- Respect privacy laws and avoid unauthorized surveillance.
Airspace Restrictions and Prohibited Areas
Many areas have restricted airspace, including airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. Always check the airspace regulations before flying.
Legal Consequences of Violations
Violating drone regulations can result in fines, suspension of operating privileges, or even criminal charges.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for keeping your drone in top condition and extending its lifespan. A proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures safety.
Regular Drone Maintenance
A scheduled maintenance plan helps prevent problems and ensures your drone remains in optimal working order.
- Inspect propellers for damage after each flight.
- Clean the drone body and sensors regularly.
- Check battery health and charge cycles.
- Inspect motors and other components for wear and tear.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Understanding common drone problems and their solutions is crucial for efficient troubleshooting.
- Battery Issues: Check battery connections, charge levels, and overall battery health.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage and ensure proper connections.
- GPS Problems: Check for obstructions and ensure sufficient satellite lock.
- Radio Control Issues: Check battery levels, antenna connections, and signal interference.
Replacing or Repairing Damaged Components, How to operate a drone
Replacing or repairing damaged components often requires specific tools and expertise. Refer to the drone’s manual for instructions and consider professional repair services if needed.
Drone Maintenance Tools and Supplies
Having the right tools readily available simplifies maintenance tasks and ensures efficient repairs.
- Screwdrivers (various sizes)
- Propeller wrench
- Cleaning supplies (soft cloths, compressed air)
- Spare propellers, batteries, and other components
Advanced Drone Techniques
Advanced drone techniques enhance your capabilities, allowing for more creative and complex flights and shots.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and effective flight, and a great resource to check out for detailed guidance is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Following these instructions will help you confidently navigate the complexities of drone piloting and ensure responsible operation.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Mastering advanced flight maneuvers such as flips, rolls, and precise hovering takes practice and skill. Start slowly and gradually increase complexity as your skills improve.
Specialized Drone Accessories
Specialized accessories such as gimbals and filters can significantly improve the quality of your aerial footage.
- Gimbals: Stabilize the camera, resulting in smoother video.
- ND Filters: Reduce the amount of light entering the camera, allowing for wider apertures and slower shutter speeds.
Creating Cinematic Drone Shots
Planning and executing cinematic drone shots requires creativity and a strong understanding of filmmaking principles. Storyboarding your shots beforehand can help achieve a cohesive and engaging final product.
Drone Software for Advanced Flight Planning
Advanced drone software enables complex flight path planning and control, allowing for precise and automated maneuvers.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding, practical skill, and a strong commitment to safety. This guide has provided a solid foundation, covering everything from pre-flight preparation and basic controls to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. Remember that consistent practice and adherence to regulations are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
So, grab your drone, review your checklist, and prepare for an exciting journey into the world of aerial exploration!
FAQ Resource
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones offer beginner modes with stability assists. Look for features like GPS, Return-to-Home (RTH), and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model and usage. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for estimated flight times; they are typically between 15 and 30 minutes.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Most drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately if you lose control. If RTH fails, try to land it manually if possible and prioritize safety.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations regarding drone registration.